Pearl - Wi-Fi Signal Strength
Table of Contents
Overview
This article is to help customers scan their wireless network in the event that the Pearl is reporting low or in some cases when the Pearl doesn't communicate due to no Wi-Fi signal.
Warning
This is only a quick guide to help customers scan their wireless network. We will not troubleshoot the apps or review the network scans.
Requirements
- Have access to a smartphone or tablet.
- Install a Wi-Fi scanning app (at the time of this writing IOS/Android store has an app called "Network Analyser")
- Access to the location where the Pearl will be installed
Steps
- Stand at the same location as where the Pearl units will be (or are) installed.
- On your smartphone, launch the wireless scanning app.
- Once the scan is done take note of the signal strength.
- You can close the apps.
- Once you have your wireless dBm value, you'll have to subtract 10dBm to it since the Pearl has a much smaller antenna than your smartphone or even laptop.
Special note
Note that the network scan can vary a lot within a day. This is due to your location and also lots of other variables from your neighborhood. You could repeat the above step during different intervals.
EX: In the below screenshot we are looking at the Wi-Fi called SMS_Pearl and the value provided from the smartphone is -60dBm, subtracting 10dBm, giving us a final value of about -70dBm.
Review your Wi-Fi signal strength
Once you have your final value, you can now review this value and see if there could be a potential issue with the Wi-FI signal strength seen at that area.
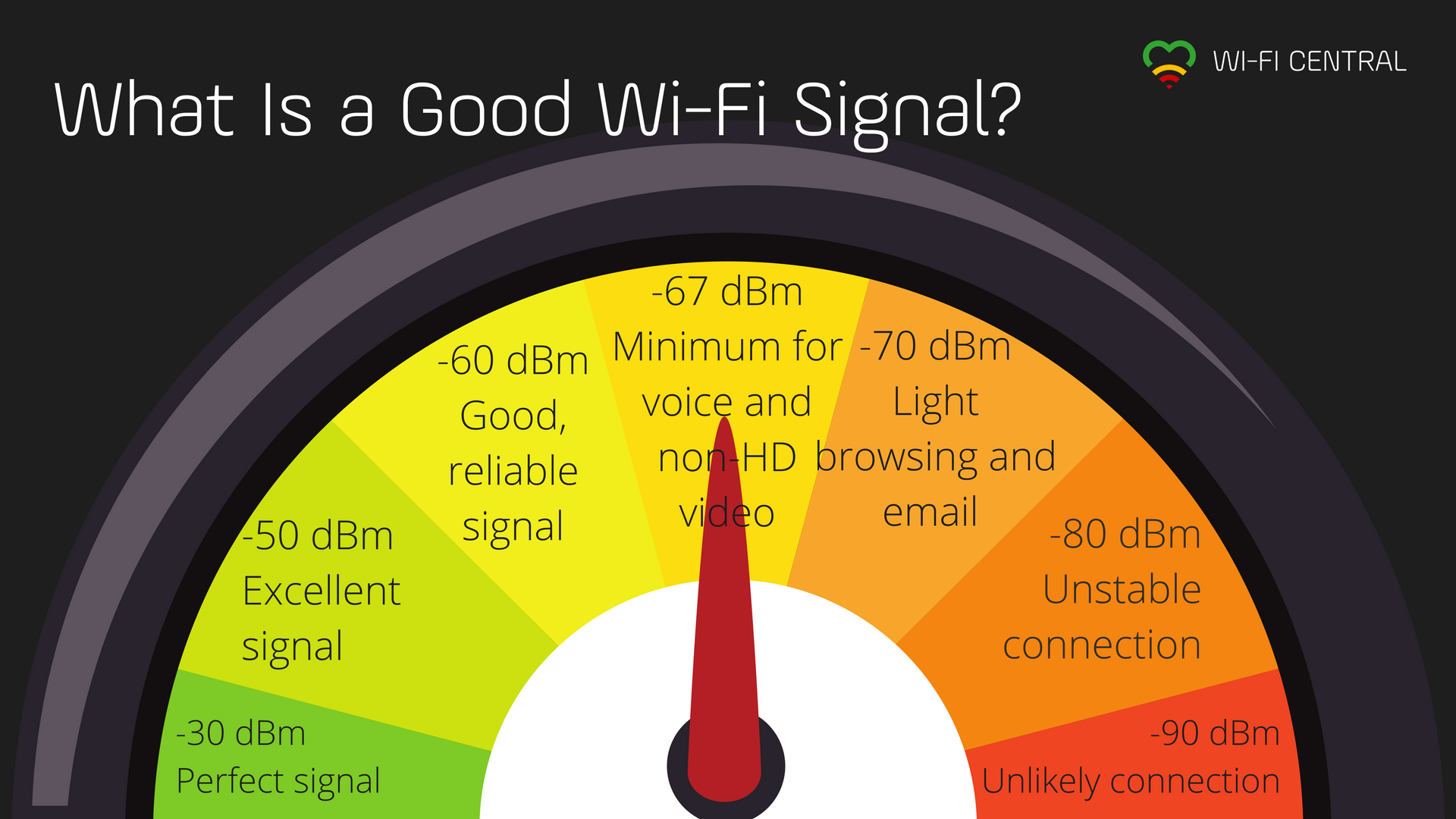
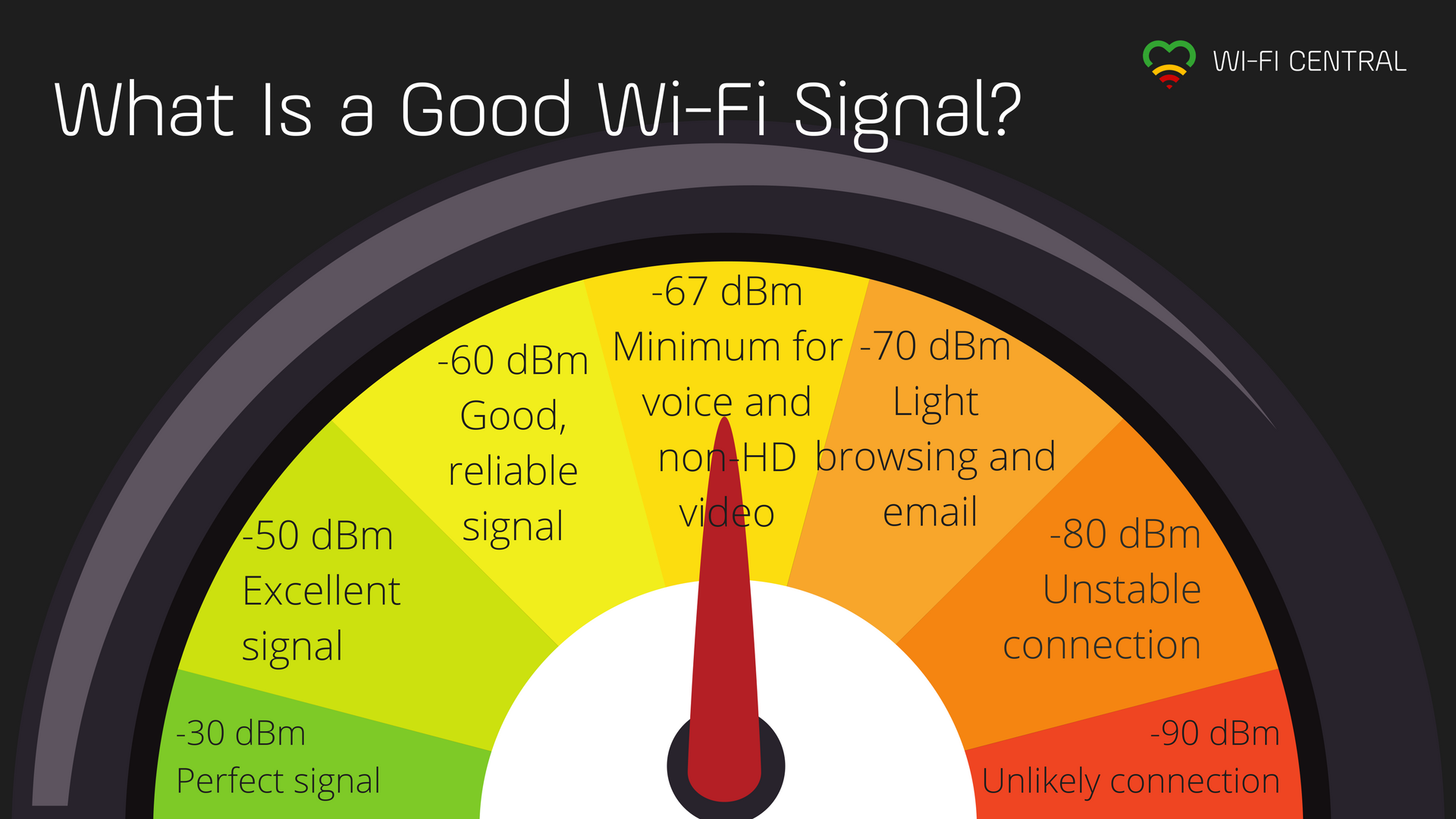
- Between 0 to -70dBm, the signal is strong enough.
- At -71dBm and less the signal strength is weak and will cause issues with the Pearl trying to connect.
Questions and Answers
Q: What if my signal is -70dBm or less?
A: You'll need to improve your signal strength or possibly add a Wi-Fi extender, details can be found here: https://help.storetraffic.com/pearl-support/pearl-adding-a-wi-fi-extender
Q: Why is my Wi-Fi not strong enough?
A: There are many factors that can impact and interfere with your Wi-Fi, some might be under your control and other factors are due to your neighbors.
Here are a few articles to help customers understand what could be the cause:
Wi-Fi - Understanding Signal Strength
Wi-Fi - Understanding Signal Strength
Overview The purpose of this article is to help customers understand Wi-Fi signal
Overview
The purpose of this article is to help customers understand Wi-Fi signals and the potential issues that could cause our devices to have communication issues.
When it comes to Wi-Fi, signal fluctuation is more common than we realize. The reason is that your Wi-Fi signal strength is constantly changing due to external conditions. Some days you're able to access the web and work without disconnecting, and other days you'll have issues just trying to stay connected and online.
This is harder to detect or diagnose if you don't have the tools. This is where we can use the Wi-Fi scanner/analyzer app to help narrow down the issues.
Signal Strength
The signal strength is the wireless signal power level received by the wireless client.
- Strong signal strength results in more reliable connections and higher speeds
- Signal strength is represented in -dBm format (0 to -100).
- The closer the value is to 0, the stronger the signal. ex: -23 dBm is better than -60dBm
Noise Level
The noise level indicates the amount of background noise in your environment.
- If the noise level is too high, it will result in degraded strength and performance for your Wi-Fi signal strength.
- Noise level is measured in -dB format (0 to 100).
- The closer the value to 0, the greater the noise level.
- Negative values indicate less background noise. ex: -80dBm is lower noise level than -10dBm.
Signal to Noise ratio
The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is the power ratio between the signal strength and the noise level.
- This value is represented as a +dBm value.
- In general, you should have a minimum of +25dBm signal-to-noise ratio. Lower than +25dBm results in poor performance and speeds.
Ex:
- If you have a -31dBm signal strength, and a -40dBm noise level, this results in a poor signal-to-noise ratio of +9dBm.
- If you have a -31dBm signal strength, and a -90dBm noise level, this results in an excellent signal-to-noise ratio of +59dBm.